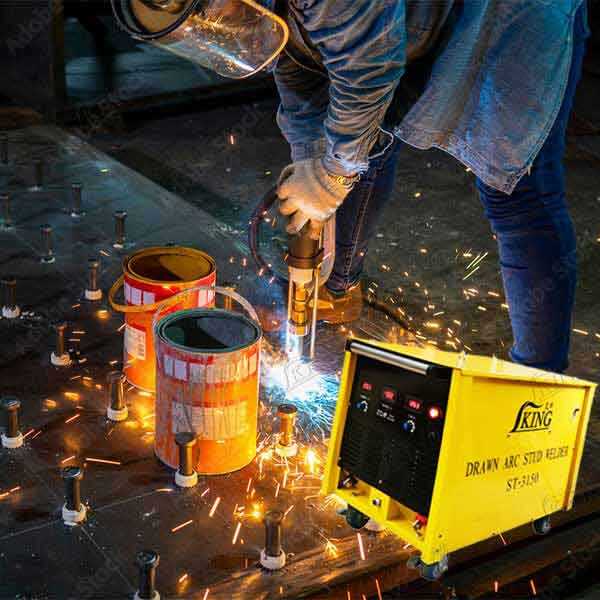
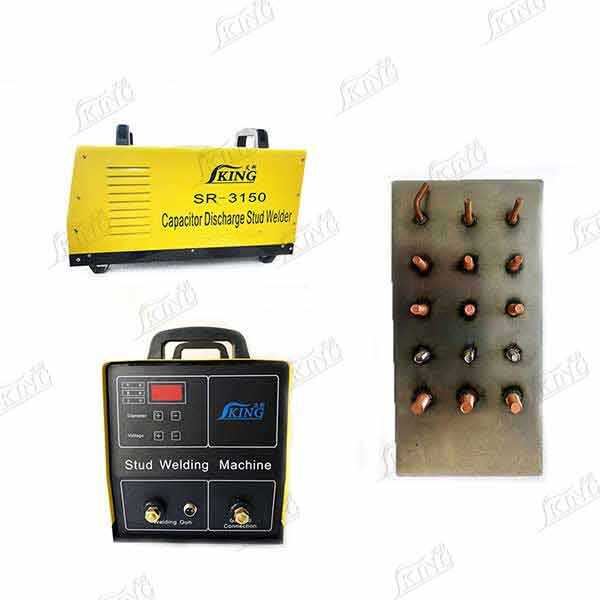
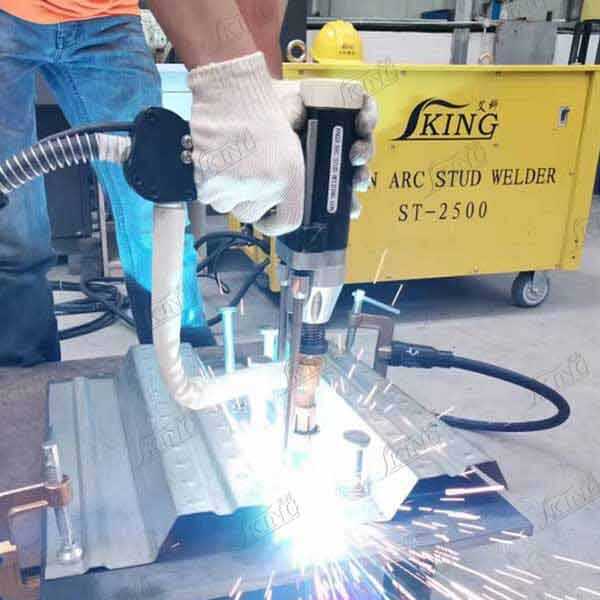
studs welding
Stud welding is a highly efficient and precise joining process that involves attaching a metal stud or fastener to a base material through a controlled welding arc. This sophisticated welding technique creates strong, reliable connections in a matter of milliseconds, making it indispensable in modern manufacturing and construction. The process begins when a stud is loaded into a specialized welding gun, which positions it against the workpiece. Upon activation, a pilot arc is established, creating a molten pool on both the stud and base material surfaces. The stud is then plunged into this molten pool, and the materials fuse together as they cool, forming a full-strength weld that's often stronger than the parent materials. This technology finds extensive applications across various industries, from automotive manufacturing and shipbuilding to construction and electrical installations. The process can accommodate different stud sizes and materials, including steel, stainless steel, and aluminum, offering versatility in application. Modern stud welding systems often incorporate advanced features such as digital control panels, precise timing mechanisms, and quality monitoring capabilities, ensuring consistent results across high-volume production runs.